④. Spring Container와 Bean
이 포스트 시리즈는 inflearn의 ‘‘스프링 핵심 원리 - 기본편 : 김영한’’ 강의와 개인적인 추가학습을 정리한 내용입니다.
4. Spring Container와 Bean
[ 정리 한 문장: Spring도 인터페이스(BeanFactory, ApplicationContext)와 구현체(ApplicationConfigApplicationContext)를 사용해 컨테이너와 빈을 사용한다! ]
스프링 컨테이너와 빈에 대해 알아보자.
1. Spring Container
-
ApplicationContext
- Bean(객체)를 등록하기 위한 공간. 엄밀하게는 상위 인터페이스인 BeanFactory가 스프링 컨테이너이지만, 우리가 사용하는 인터페이스는 ApplicationContext이므로, 보통 이 것을 Spring Container라고 많이 부른다. (BeanFactory는 아래에서 다시)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);-
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext는ApplicationContext인터페이스의 구현체. -
파라미터로 구성(설정)정보가 담겨있는 클래스를 전달받는다.
-
스프링 컨테이너 생성과정
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(---.class);를 통해 스프링 컨테이너 생성.- 컨테이너는 {빈 이름 : 빈 객체 } 의 key : value 형태로 구성되며, 빈 이름은 메서드 이름, 빈 객체는 메서드 안에서 생성되어 리턴된 객체를 담음. (빈 이름은
@Bean(name="새로운이름")으로 새로 부여 가능)
*빈 이름은 항상 달라야 함! 아니면 값이 덮이거나 설정 오류 발생 - 파라미터로 전달받은 클래스에 접근하여 코드를 읽어 Bean을 이름 : 객체 형태로 저장.
- 구성(설정) 정보를 참고하여 의존관계까지 주입함. (개념상 그렇지만, AppConfig와 같이 직접 등록하는 경우에는 빈 생성과 의존관계 주입이 한번에 처리되기도 함)
2. Container의 Bean 조회
-
.getBeanDefinitionNames(): 컨테이너에 등록된 모든 빈 이름을 조회. 컨테이너에서의 ‘Key’가 됨..getRole(): 빈의 역할을 조회.- ROLE_APPLICATION - 직접 등록한 애플리케이션 빈.
- ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE - 스프링 내부에서 사용하는 기본 빈.
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); @Test @DisplayName("애플리케이션 빈 출력하기") void findApplicationBean() { String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) { BeanDefinition beanDefinition = ac.getBeanDefinition(beanDefinitionName); if (beanDefinition.getRole() == BeanDefinition.ROLE_APPLICATION) { Object bean = ac.getBean(beanDefinitionName); System.out.println("name = " + beanDefinitionName + " object = " + bean); } } } -
.getBean(): 빈 이름으로 빈의 객체(인스턴스)를 조회..getBean(BeanName, Type);- 조회 대상 빈이 없는 경우
'NoSuchBeanDefinitionException'예외 발생
- 조회 대상 빈이 없는 경우
.getBean(Type);- 타입으로만 조회 시
'NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException'예외 발생 - 이럴 경우, 조회하고자 하는 객체의 구체타입(구현체)을 명시하거나 빈 이름으로 조회하면 됨. 단, 구체타입(구현체)을 명시하는 것은 구현체를 의존하는 코드라 좋은 코드는 아님. (우리가 이때까지 인터페이스에 의존하고자 그렇게 노력했지 않는가)
- 타입으로만 조회 시
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); @Test @DisplayName("빈 이름으로 조회") void findBeanByName() { MemberService memberService = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberService.class); assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class); } @Test @DisplayName("빈 타입으로만 조회") void findBeanByType() { MemberService memberService = ac.getBean(MemberService.class); assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class); } @Test @DisplayName("구체 타입으로 조회") void findBeanByName2() { MemberService memberService = ac.getBean("memberService", MemberServiceImpl.class); assertThat(memberService).isInstanceOf(MemberServiceImpl.class); } @Test @DisplayName("빈 이름으로 조회X") void findBeanByNameX() { // 예외처리 됨 // MemberService memberService = ac.getBean("memberServicexxx", MemberService.class); assertThrows(NoSuchBeanDefinitionException.class, () -> ac.getBean("memberServicexxx", MemberService.class)); } -
Bean 조회 시, 부모 타입으로 조회하면 자식 타입은 줄줄이 따라나와 조회됨. -> Object 타입으로 조회하면 모든 스프링 빈이 조회됨.
3. BeanFactory
-
스프링 컨테이너의 최상위 인터페이스. 빈을 관리하고 조회하는 역할.
-
우리가 사용했던
.getBean()의 메서드를 제공함! -
실무에서는 BeanFactory는 거의 사용하지 않음. 왜? 스프링 빈을 사용하기 위해 여러 부가기능이 필요하기 때문이고, 그러한 역할들을 모두 담은 인터페이스가 바로
ApplicationContext임.*Q.
ApplicationContext가 추가로 구현하고 있는 대표적인 역할은? -MessageSource,EnvironmentCapable,ApplicationEventPublisher,ResourceLoade등.
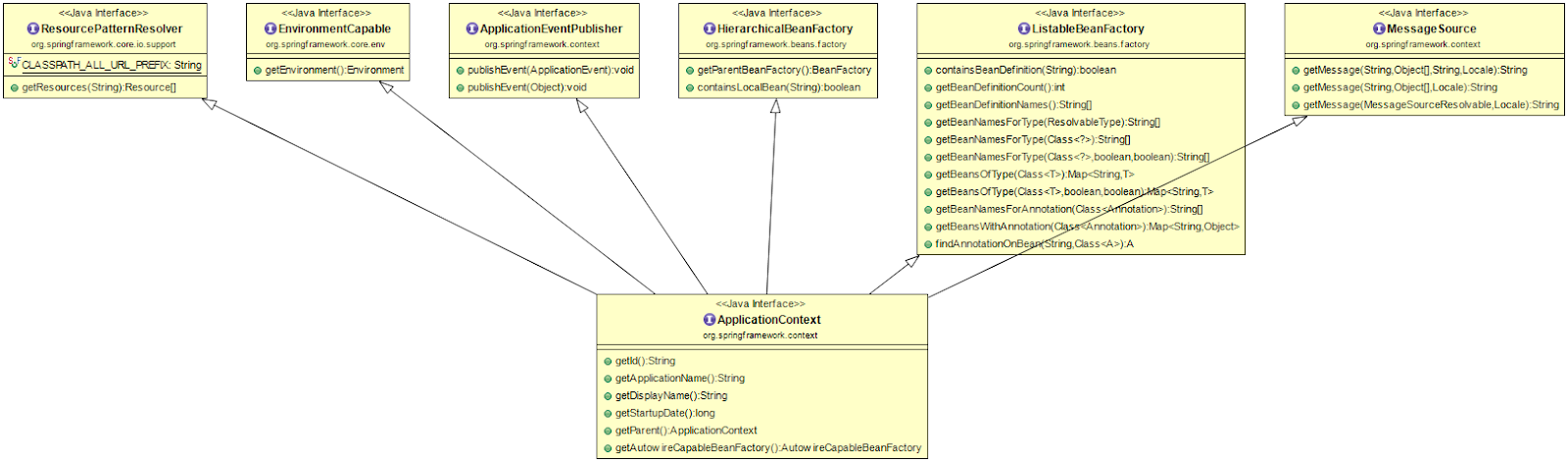 출처: [https://www.javaguides.net/2019/04/spring-applicationcontext-interface-api.html]
출처: [https://www.javaguides.net/2019/04/spring-applicationcontext-interface-api.html]
4. BeanDefinition
- 빈 설정 메타정보.
- 스프링 역시 이러한 기능을
BeanDefinition이라는 역할(인터페이스)을 의존하여 지원함. ApplicationContext(구현체)는 구성(설정)파일로 접근하여(ex, AppConfig.class) 코드를 읽은 후BeanDefinition이라는 빈 메타정보를 생성하여 리턴함. 이게 컨테이너에 전달되는 것임.- 이 안에는 BeanClassName, factoryBeanName, Scope 등의 여러가지 정보가 들어있음.
마지막 수정일시: 2022-08-11 14:10

댓글남기기